Author: Kevin Li Source: substack, @kevinlhr88 Translation: Shan Ouba, Jinse Finance
A deep dive into Strategy (formerly MicroStrategy), the creator of the Bitcoin Treasury model . Last week we shared a deep dive into CoreWeave. This week, as the “Digital Asset Treasury” continues to gain traction, we turn our attention to Strategy .
summary
Bitcoin is entering its institutional era , driven by spot ETF approvals and accelerated global adoption in 2024. But the transition to mainstream store of value is still in its early stages.
The core investment philosophy of the Strategy is based on the long-term compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of Bitcoin. This growth rate is currently about 40-50%, and is expected to gradually decline in the future, tending to a level linked to inflation. Most of its appreciation will come from the depreciation of fiat currencies and the continued allocation of institutional funds.
Strategy is not just a Bitcoin holding tool, but more like a securities company backed by Bitcoin . It uses long-term, non-redeemable capital to continuously purchase Bitcoin through convertible bonds, preferred stocks, and ATM (at-market) stock plans.
Convertible bonds provide liquidity linked to the appreciation of Bitcoin, allowing companies to "use bonds to buy coins now and redeem stocks in the future." The structural design is suitable for hedge funds to conduct volatility arbitrage or implement delta neutral strategies.
The preferred shares open up the $46 trillion U.S. bond market for Strategy, providing institutional investors with a fixed-income product backed by Bitcoin that combines yield and inflation protection.
ATM Stock Issuance Program : Real-time financing when market sentiment is positive and stocks are trading at a premium (mNAV > 1), further increasing the number of bitcoins per share and enhancing shareholder value.
Today, Strategy's stocks have become a customized Bitcoin financial product , covering the risk spectrum from high-volatility equity assets to stable fixed-income instruments, meeting the allocation needs of different institutional funds. The core logic of this flywheel model is that the long-term CAGR of Bitcoin must be higher than the cost of funds .
Once this condition fails, the company will face dilution risk and leverage pressure. To continue to grow, the company needs execution, brand trust and institutional confidence as support.
Part 1: Bitcoin Investment Logic
Before evaluating Strategy, we first need to establish a basic understanding of Bitcoin. The entire strategic foundation of Strategy is entirely based on the long-term compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of Bitcoin in the next ten years .
Bitcoin is currently in the process of transitioning from an “emerging, fringe asset class” to a “core component of the global financial system.” This transition can be said to begin with the official approval of a spot Bitcoin ETF in 2024. Currently, this transition process is entering its second year, and we are still in the early stages.
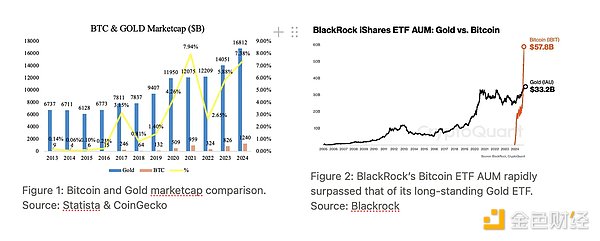
To better understand the current situation: Bitcoin has surpassed $100,000, setting a new all-time high, but its total market value is still only about 7% of gold . At the same time, gold prices are also close to all-time highs due to rising global uncertainty. This high attention to gold is not a resistance to Bitcoin, but rather a sign of an overall increase in market demand for "value store assets", and Bitcoin is a direct beneficiary of this trend.
Furthermore, within a year of its launch, BlackRock’s Bitcoin spot ETF has surpassed its gold ETF, which has been launched for ten years, in terms of assets under management , which fully demonstrates that investor preferences are rapidly shifting towards Bitcoin, and it is gradually becoming a “modern value reserve tool.”
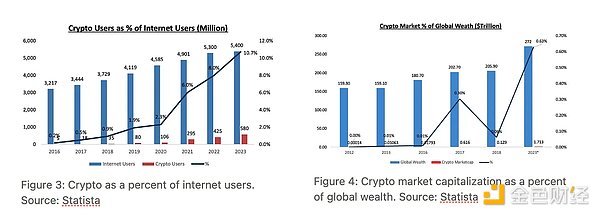
We are also witnessing a rapid growth in cryptocurrency users: by 2023, global crypto users account for nearly 10% of global Internet users. However, at the same time, crypto assets account for only 0.63% of global wealth, which shows that crypto assets (especially Bitcoin) still have huge room for growth.
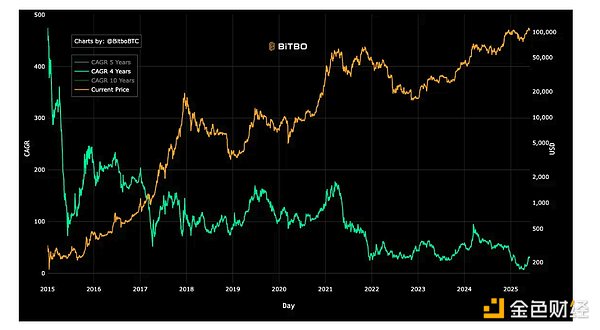
Historically, Bitcoin’s early CAGR once exceeded 100%. However, as it matured, this figure gradually declined and is currently in the 40-50% range. It is expected that in the next decade, the CAGR will continue to decline, possibly from 50% to 40%, then to 30%, and then to 20%, and eventually approach the inflation rate, converging with traditional financial assets and becoming part of the global asset allocation system.
Part 2: Core drivers of Bitcoin price
As a scarce and non-interest-bearing asset, the long-term price of Bitcoin is driven primarily by two factors:
1. Fiat currency depreciation/inflation
The continued expansion of the supply of fiat currencies, especially the U.S. dollar, has led more and more investors to seek assets that resist inflation. The total amount of Bitcoin is fixed at 21 million , so it is regarded by more and more investors as a reliable "digital gold".
In an interview with Lex Fridman, Michael Saylor clearly expressed this logic: Over the past 100 years, the real annual inflation rate in the United States has been about 7–8% , much higher than the 2% claimed by the government. He pointed out that the government has systematically underestimated real inflation by changing the CPI commodity basket and the "hedonic adjustment method". Real inflation is often reflected in asset prices such as housing prices, stock markets, and bond markets - and these assets are not counted by the CPI.
2. Global investors’ preference for Bitcoin assets increases
Another key driving factor is the increasing proportion of Bitcoin in investors’ portfolios. ETFs have become a bridge between the crypto market and the traditional financial market, providing a safe, compliant and scalable investment tool.
According to data from CoinShares and Bloomberg, Bitcoin ETFs in the United States are increasingly held by professional investors, with financial advisors and hedge funds being the main driving force . Although pension funds are still limited in their participation, their entry could trigger a new wave of major institutional adoption.
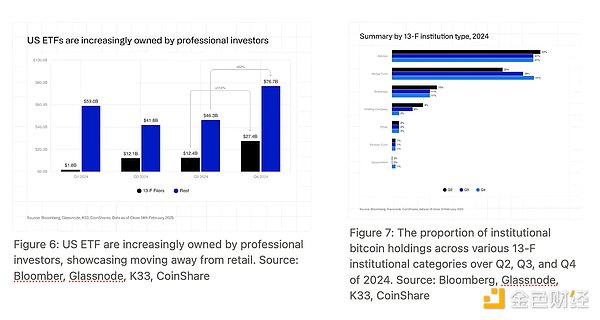
In summary, if the average CAGR of Bitcoin in the future is 40% , about 7-8% can be attributed to the depreciation of fiat currency, and the remaining 32-33% comes from the increase in the proportion of investors' allocation. This decomposition is crucial to understanding the long-term investment logic of Strategy, and will be further analyzed later.
Strategy Brief: A Toolbox to Unlock More Capital
Originally a business intelligence and data analytics platform, Strategy is now better known as a pioneer in enterprise Bitcoin adoption .
Since 2020, the company has begun to allocate Bitcoin on a large scale as its core treasury asset. Thanks to this strategy, its stock price performance has surpassed all members of the so-called "Magnificent Seven" and has become one of the best performing stocks in the past few years.
Although on the surface Strategy appears to be just a Bitcoin holding company, a deeper analysis reveals that it is essentially a "securities company with Bitcoin as its underlying asset."
Its core goal is to continuously raise funds to acquire more Bitcoin through various non-redeemable liquidity instruments in the financial market. Through this mechanism, Strategy actually opens up a new type of company: we can call it a "Bitcoin vault company."
Its sole goal: to increase the number of bitcoins represented by each share of its publicly traded stock .
Currently, Strategy raises funds mainly through the following three methods:
Convertible Bonds
Issue bonds and purchase Bitcoin after raising funds;
In the future, creditors can choose to convert bonds into stocks, which is suitable for volatility arbitrage and hedging strategies.
Preferred Stock
Issue preferred stocks with fixed dividends every year to attract institutional funds seeking fixed income;
Similar to a bond but without the redemption obligation.
Issue at market price
Sell new shares in real time through exchanges when market demand is strong and the stock price is higher than the intrinsic value;
Raise funds quickly and flexibly, and use them directly to buy more Bitcoin.
Strategy's Convertible Bonds
The first tool Strategy uses to obtain liquidity is a convertible bond (CB). This type of debt instrument allows the company to borrow non-redeemable funds, usually for a period of four years, at a very low annual interest rate. Each bond contains a conversion price, which is the target share price at which the debt can be converted into equity. If Strategy's stock price does not reach this price, the company must repay the principal and interest at maturity.
This structure is particularly attractive to institutions seeking to hold Bitcoin for the long term and reduce risk. In addition, some institutions that are unable to purchase Bitcoin directly due to regulatory restrictions can still obtain indirect investment by investing in these convertible bonds. As the price of Bitcoin rises, Strategy's shares generally appreciate as well, allowing bondholders to convert bonds into shares and obtain upside gains. Even in the event of a decline, investors can still receive principal and interest, providing a more balanced risk-return. Historically, these convertible bonds have even outperformed the spot performance of Bitcoin.
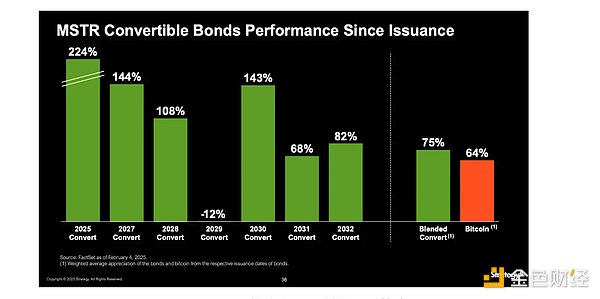
Figure 9: MSTR convertible bond performance
Since convertible bonds essentially function like long-term call options, if the convertible bonds are converted, Strategy is actually selling its shares at a higher future price and using this liquidity to buy Bitcoin in the present - which is exactly where Strategy's value accrues. Even more interestingly, due to the structure of these bonds, Strategy's shares become safer as the stock price rises. This is because the company gains the ability to convert outstanding debt into equity, effectively removing these liabilities from its balance sheet. In addition, if the stock price exceeds 130% of the conversion price within a certain period of time, Strategy can force bondholders to redeem their shares or accept cash repayment.
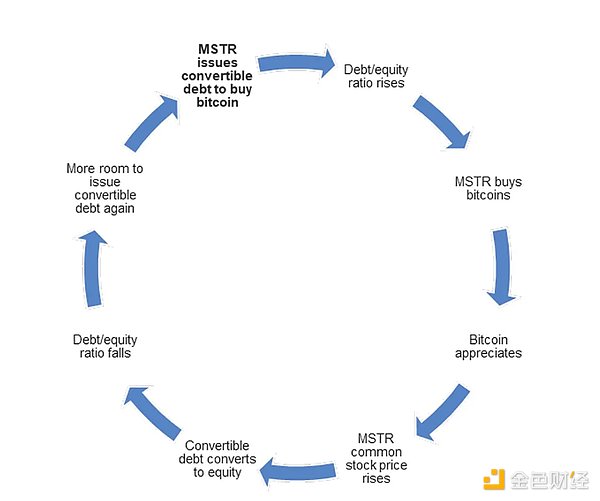
Figure 10: MSTR Convertible Bond Bitcoin Strategy Source: Bitwise
It is important to emphasize that these bonds are unsecured, meaning they are not backed by collateral. Even if the price of Bitcoin drops by 90%, Strategy will not face the risk of a margin call as long as the price recovers before the bond maturity date. To manage this risk, Strategy strategically extends the maturity of bond issuances, typically spreading them over two Bitcoin cycles, making the repayment risk more manageable over time.
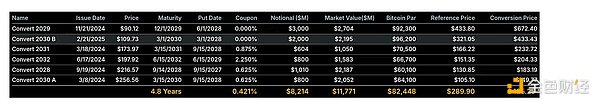
Figure 11: Current strategy convertible bond issuance, highlighting convertible bonds with low issuance rates (coupon rates) and maturities spread across multiple Bitcoin market cycles.
As Strategy moves into new financial sectors, it has effectively found a way to package its equity volatility into products and sell it to institutions through convertible bonds - often with zero coupon terms (as shown above). When Strategy issues convertible bonds to buy Bitcoin, it is actually using debt leverage to acquire a volatile asset. This leverage increases the volatility of its own stock because the company takes on margin-like risks.
Since convertible bonds (CBs) are priced similar to options, institutional investors (hedge funds in this case) often hedge their exposure by short Strategy's stock when buying the bonds. This creates a delta-neutral position, eliminating directional risk while maintaining exposure to realized and implied volatility. Hedge funds profit through gamma trading and vega exposure , taking advantage of Strategy's large price movements and leveraged balance sheet.
Example of a hedge fund arbitrage operation: For example, if the stock price rises from $400 to $500, the bond's Delta value may rise from 0.7 to 0.9. To remain delta neutral, the fund short more shares at $500. If the stock price subsequently falls back to $400, the fund will cover the short position, locking in profits. However, if the price continues to rise, the value of the bond will offset the short loss. These fluctuations, which can occur multiple times per month, can generate continuous profits. As Strategy issues more bonds, its stock volatility will increase, which can increase the value of the convertible bond through higher implied volatility. This creates an attractive arbitrage opportunity for hedge funds.
Ultimately, convertible bonds (CBs) create a win-win situation for Strategy and CB buyers: hedge funds can arbitrage volatility, while Strategy can gain future liquidity.
Here is an example of unit economics for Strategy’s CB value accumulation:
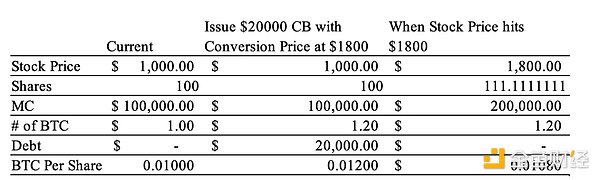
Figure 12: Example of price increase per Bitcoin via convertible bond conversion
For this example, we assume that Strategy has a share price of $1,000, 100 shares outstanding, and that it invests its entire $100,000 market cap in Bitcoin at $100,000 per Bitcoin — meaning that the company holds 1 Bitcoin. Next, Strategy issues a $20,000 convertible bond (CB) with a conversion price of $1,800. The company uses the proceeds to purchase more Bitcoin, increasing its total Bitcoin holdings. When the share price reaches $1,800, the bond converts to stock, increasing the number of shares from 100 to approximately 111.11 ($20,000/$1,800). After the conversion, the company's Bitcoin holdings increase from 0.01 Bitcoin per share to approximately 0.0108 Bitcoin per share — meaning an increase in shareholder value.
Strategy Preferred Stock
Strategy's next step to gain greater liquidity is to issue preferred shares - structured like fixed income products, targeting the larger fixed income market. By comparison, the U.S. convertible bond market is about $270 billion to $280 billion, while the U.S. fixed income market is about $46 trillion, with about 100 times the available liquidity in the convertible bond market.
Strategy currently offers three types of preferred stocks:
STRK – Series A Perpetual Executive Preferred Stock – offers 8% yielding, convertible, redeemable shares to provide long-term funding for Bitcoin accumulation.
STRF – Series A Perpetual Conflicted Preferred Stock – provides 10% yielding, non-convertible, non-redeemable shares, ensuring stable, long-term capital for Bitcoin purchases.
STRD – Series A Perpetual Stride Preferred Stock – offers 10% yielding, non-convertible, redeemable shares that provide stable, long-term capital for Bitcoin purchases.
Each bond has a par value of $100. STRK pays a $2 dividend quarterly ($8 per year), while STRF and STRD pay $2.50 per quarter ($10 per year). STRK is also convertible, with a conversion target of $1,000 in MSTR shares, offering holders potential upside in both MSTR and Bitcoin. In contrast, STRF is non-convertible and non-redeemable - offering higher and more stable returns, but without upside. The main differences between STRF and STRD are callability and dividend treatment: while STRD also offers a 10% yield, it is callable and pays non-cumulative dividends - missed or delayed payments do not accumulate, increasing investor risk. STRF, on the other hand, pays cumulative dividends - any missed payments accrue interest, which must eventually be paid by the Strategy.
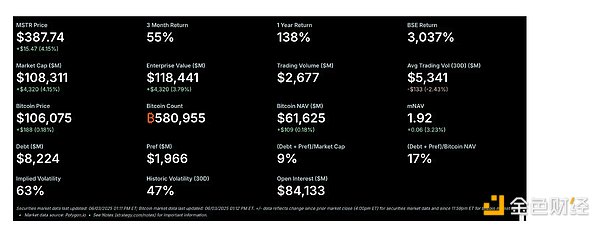
Figure 13: The convertible bonds and preferred stocks on Strategy’s balance sheet only account for 9% of the company’s market value, indicating that leverage is under control. Source: Strategy
STRK is priced at a combination of the risk-free rate and the market price of MSTR. As MSTR approaches $1,000, STRK should rise in value due to its convertible nature. Furthermore, in finance, returns are relative. If the risk-free federal funds rate were to fall from its current range of 4.5%-5% to a lower range of 2%-2.5%, STRK's theoretical return should fall to around 4%. For this to happen, STRK's market cap would need to rise to around $200 per share to reflect the fall in yield and maintain price equilibrium.
This creates two clear upside scenarios for STRK holders:
Falling interest rates – As interest rates fall, STRK appreciates in value.
MSTR price increase – If MSTR reaches $1,000, STRK will benefit due to its conversion function.
As Jeff Parks said, STRK is "the perfect financial product." Investors can earn an 8% annual return while also benefiting from falling interest rates or appreciation in MSTR. Even without either catalyst, investors can still gradually recover their principal through an 8% annual return.

Figure 14: STRK’s performance and trading statistics demonstrate its high-performing fixed income products. Source: Strategy
In contrast, STRF and STRD are priced purely on the risk-free rate. If the risk-free rate falls to 2%-2.5%, these securities are also expected to trade closer to $200 to reflect the new yield of about 5%, down from the current 10%.
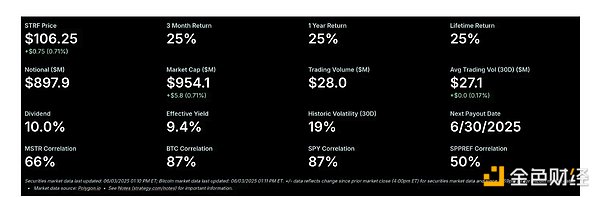
Figure 15: STRF’s performance and trading statistics also demonstrate its high-performing fixed income products. Source: Strategy
However, STRD is typically priced at a discount to STRF, resulting in a higher yield. This is because STRD is redeemable first and its dividends are non-cumulative, meaning investors are not guaranteed to receive the stipulated dividends if they are not paid on time. This structural difference justifies the yield premium that investors demand to hold STRD over STRF. However, because the dividends come from MSTR stock issuance, as the price of MSTR and Bitcoin continue to rise, the relative impact of annual interest payments on total issuance becomes increasingly smaller, resulting in minimal equity dilution over time.
Here is an example of the unit economics of STRK preferred stock:
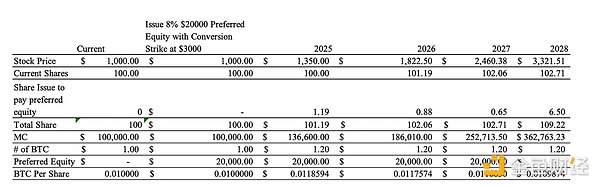
Figure 16: Example showing the increase in the price of Bitcoin per share through the issuance of STRK
In this case, MSTR's share price starts at $1,000, increases by 35% per year, and initially issues 100 shares with a market cap of $100,000 - all backed by one Bitcoin. The company raises $20,000 by issuing 8% preferred stock to buy more Bitcoin.
Each year, 8% interest on the preferred stock will be paid to STRK shareholders through the issuance of new MSTR shares. The conversion price of the preferred stock is $3,000. By 2028, the stock price reaches $3,321.51, triggering the conversion of all $20,000 of preferred stock into common stock.
The total number of shares increases due to the issuance of new shares each year to pay interest, as well as upon conversion. The price per Bitcoin is recalculated annually based on the updated total Bitcoin holdings and number of shares. By 2028, the price per Bitcoin has increased from 0.01 Bitcoin/share to 0.0109874 Bitcoin/share, an increase of nearly 10%. This highlights how the strategy of using preferred shares to increase Bitcoin holdings can increase Bitcoin holdings per share, even after accounting for dilution.
As mentioned earlier, fundamentally, the price of Bitcoin is driven by two core factors: monetary inflation and people's growing preference for Bitcoin as an asset. Strategy's approach to these preferred stock products essentially gives up some of the inflation-driven upside in exchange for providing preferred shareholders with a yield - in the case of STRK, specifically an inflation-linked yield. This structure allows the company to arbitrage the dividends paid by the preferred shares against the compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of Bitcoin. As long as the CAGR of Bitcoin exceeds the effective cost of capital (e.g. 8-10%), these preferred stock instruments will make economic sense. In this sense, the newly constructed preferred stock issuances act like true inflation-protected bonds, making them attractive to fixed income portfolio managers seeking exposure to hard asset-backed income.
Here is an example of the unit economics of STRF preferred stock:
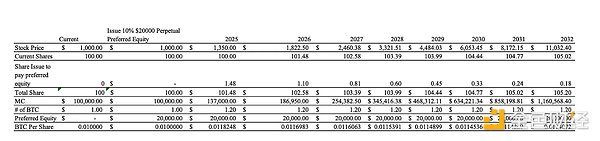
Figure 17: Example of the increase in the price of Bitcoin per share through the issuance of STRF. Note that the number of shares issued to pay the dividend decreases exponentially.
The unit economics of STRF and STRD are very similar to STRK, but with one key difference: STRK converts fully to equity by 2028, while STRF is perpetual and STRD is redeemable at the company's discretion.
As of 2025, Strategy seems to prefer preferred stocks as its preferred method of leverage. A key advantage is that preferred stocks generally have no maturity date, thus avoiding the pressure of refinancing or repayment risk. In addition, the annual interest rate of such preferred stocks is relatively low compared to the company's market value and scale of operations. The strategy implicitly indicates that Strategy is preparing for a long-term Bitcoin super cycle (rather than the traditional four-year Bitcoin cycle).

Figure 18: In Strategy’s new 42/42 capital plan, Saylor is focusing on fixed income products, especially STRK. Source: Strategy
Strategy Market Release
The third, but arguably most important/most frequently used, of Strategy's liquidity tools is its At-The-Market (ATM) program. Unlike convertible bonds or preferred stocks (structured, negotiable securities), the ATM program allows Strategy to sell newly issued shares directly into the open market in real time, typically through a designated broker. This provides the company with flexible, on-demand access to capital based on current market conditions.
Due to the use of convertible bonds and preferred shares, Strategy has managed to earn a premium above its net asset value (NAV) because investors believe that each share will represent more Bitcoin in the future. In addition, this NAV premium is affected by Strategy's leveraged balance sheet and the volatility it generates. This premium is dynamic - it can expand or contract based on broader market liquidity and investor risk appetite. When risk-on sentiment is dominant and Strategy's strategy is favored, the premium will expand. When the market tightens or sentiment subsides, the premium may shrink. Strategy can take advantage of this volatility through its ATM program.
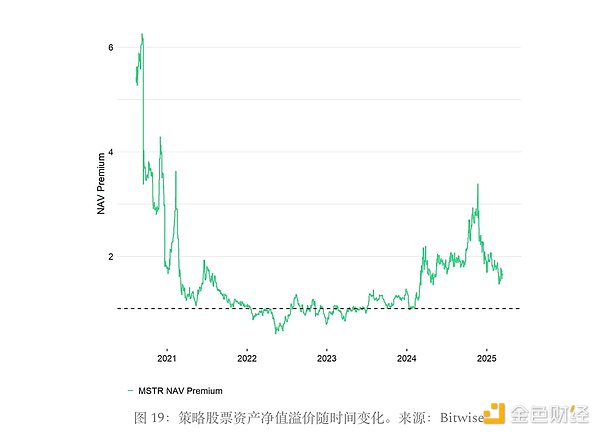
Issuing new shares is accretive when the price-to-book value (mNAV) ratio is greater than 1 due to volatility and market optimism. Strategy is effectively selling shares that represent fewer bitcoins than the company could purchase with available proceeds, thereby increasing the value of each bitcoin. In this way, the ATM program is more than just a financing tool, it is an execution trigger for Strategy's capital flywheel, allowing the company to respond in real time to favorable market conditions and expand its bitcoin holdings with high capital efficiency.
Part 3: Equity as a Product and Growth Engine
This ability to issue shares at a premium to NAV — effectively selling volatility in exchange for Bitcoin — reveals a deeper insight: Strategy’s shares are no longer just shares, they have become a financial product. For its debt products, value is not accrued at issuance, but when Strategy sells shares at a price consistent with the future and uses that liquidity to buy Bitcoin immediately. Essentially, the company is offering a new type of security: future/premium MSTR shares backed by Bitcoin, structured to capture forward-looking BTC exposure with institutional leverage.
Productizing Bitcoin through equity packaging to suit different types of investors
As briefly discussed in the convertible bond section, Strategy’s real innovation is its ability to productize Bitcoin investment and create customized compliant financial products - using its secondary equity as a structural wrapper. Pension funds, insurance companies, endowments, and bond portfolio managers are generally prohibited from directly holding Bitcoin. By issuing convertible bonds and preferred stocks, Strategy unlocks indirect investment in Bitcoin for these institutional investors.
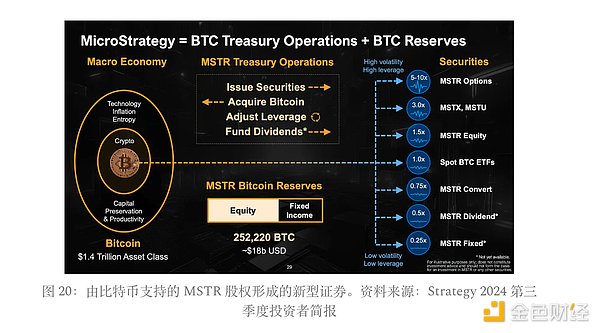
Furthermore, these institutions have very different return and volatility needs. A bond portfolio manager will not allocate to a crypto asset with an annualized return of 40% if the volatility is also 40%. They would rather hold a preferred stock instrument with an internal rate of return (IRR) of 10% and a volatility of only 10%. Because of this, Strategy’s capital instruments – convertible bonds and its different preferred stock classes – are deliberately structured to provide different risk/return characteristics.
On one hand, MSTR shares offer the highest expected return and volatility. On the other hand, STRF offers the lowest return and lowest volatility, functioning more like a fixed-income instrument. In between are convertible bonds (CBs) and other preferred products that offer tailored exposure to a specific institution’s risk appetite, effectively making Strategy a menu of Bitcoin-wrapped securities for a variety of risk profiles.
Volatility is vitality
Volatility is a key component of the Strategy flywheel. On one hand, MSTR can take advantage of rising volatility by issuing shares when mNAV is high through its ATM program, effectively monetizing its premium. On the other hand, higher volatility can improve the pricing of convertible bonds because it increases the value of the embedded call option.
Additionally, increased volatility has boosted liquidity in MSTR shares, its options, and derivatives, enabling hedge funds to employ gamma trading strategies and construct zero-coupon convertible bonds. The greater the volatility, the greater the profit potential of gamma trading, further strengthening institutional demand. Finally, leveraged products such as MSTZ and MSTX also benefit from this liquidity dynamic. They allow for higher exposure and, in turn, attract more capital into the strategic stock ecosystem, thereby enhancing overall market depth.
mNav is the fuel for your engine
mNAV is the driving force behind Strategy's accumulation of Bitcoin. In our unit economic models for convertible bonds and fixed income products, we assume an mNAV of 1. But when a company issues shares at a premium (mNAV > 1), its value compounds faster, allowing it to raise more capital at more favorable terms and more effectively increase the value of each BTC share.
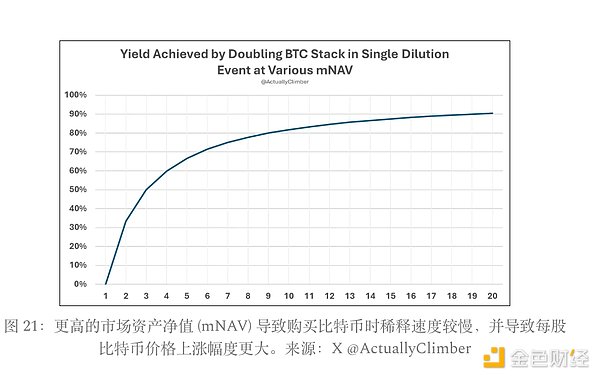
Why the market pays a premium
Several factors contributed to this outcome. First, the company expected to receive more Bitcoin per share from the liquidity raised through convertible bonds and preferred shares. In addition, in the early days of the strategy, regulatory restrictions prevented many institutional investors from directly holding Bitcoin/Bitcoin ETFs, making the Strategy Strategy an alternative strategy. This alternative value remains relevant, depending on the institutional profile. Second, brand trust is critical: do institutions trust the company's financial products? Do retail investors buy into its narrative? Both play a role in maintaining the premium as equity becomes the engine of the strategy. Strategy Strategy excels in communicating its vision to both institutional and retail investors. In addition, Strategy Strategy also has a strong first-mover advantage - being the first to offer a safe and reliable Bitcoin-backed equity product can build brand equity that competitors will find difficult to match. Institutions are unlikely to support convertible bonds or preferred shares issued by second-tier players - credibility and market leadership are critical in this space.
Passive Inflows: The ETF Feedback Loop
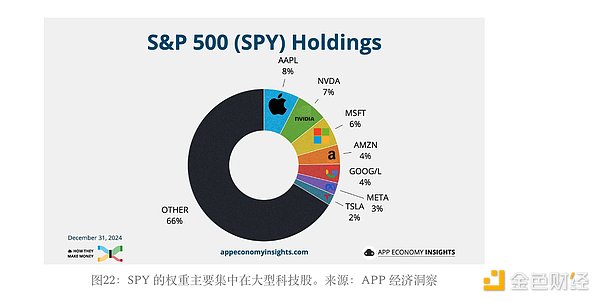
Another very interesting fact is that financial markets have gradually shifted from active to passive investing, largely due to the rise of market-cap weighted ETFs. In this model, the larger your market cap, the more ETF allocation you get. Strategy can strategically employ its ATM program around ETF inclusion or rebalancing events. Buying pressure from ETFs can offset the dilution effect of ATM issuance. As Strategy issues more shares, its market cap grows, which triggers more ETF demand, which allows further ATM issuance - a self-reinforcing cycle. Last year, Strategy announced $21 billion in ATMs and a $21 billion debt capital structure. In the fourth quarter of 2024, the company issued more than $15 billion in shares (an unprecedented amount), coinciding with its inclusion in the QQQ ETF. The next major catalyst could be the S&P 500 (SPY) inclusion expected in September this year, another trigger that could trigger a major accumulation of Bitcoin.
Risks of Strategy Models
The most critical risk for Strategy’s “capital flywheel” model—and arguably the only risk that really matters in the long run—is that Bitcoin’s internal rate of return (IRR) is lower than the company’s cost of capital.
If the annualized return on Bitcoin is less than 10%, then the preferred stock holders (such as STRK or STRF) will receive more than the appreciation of Bitcoin itself, resulting in the company's inability to create value for common shareholders. Similarly, the issued convertible bonds (usually with a term of 4-5 years) also rely on Bitcoin's annualized compound interest exceeding 10% to achieve a conversion with an appreciation effect. Otherwise, Strategy is left with only debt, and there is no increase in "Bitcoin per share".
In this case, the company's leverage ratio becomes extremely critical. If Bitcoin performs poorly and the leverage ratio is high, even if there is no risk of liquidation, financial strain will be caused by future debt repayment pressure or further dilution. One cycle may be able to survive, but if Bitcoin performs poorly for multiple consecutive cycles, the "flywheel" mechanism will fail. Whether the entire model can be established depends on the premise that the long-term return of Bitcoin continues to be higher than the capital cost used to purchase it.
The final key risk is that Strategy's brand and investor confidence are closely tied to Michael Saylor. His leadership and strong stance on Bitcoin are core pillars of the company's image. If he leaves for personal reasons, health issues, or damage to his reputation, it could quickly erode market trust, affect access to capital, and jeopardize the ability to maintain the company's mNAV premium, ultimately shaking the foundation of the flywheel model.
Global Opportunity: The Rise of Bitcoin Vault Companies
Looking ahead, given the differences in financial regulatory systems across regions, there may be multiple “regional versions of Strategy” – companies that provide Bitcoin investment exposure through equity structures that comply with local regulatory requirements.
One case worth noting is Metaplanet , which is positioning itself as the “Japanese version of Strategy” and may become an important player in this field by leveraging Japan’s low capital costs and “yield-hungry” investment environment.
Can Ethereum and Solana replicate this model?
Recently, some people have tried to build a "treasury company" similar to Strategy for Ethereum (ETH) or Solana (SOL) . But from a first principles perspective, the key question is: Are institutions willing to buy convertible bonds or preferred stocks backed by these assets?
The reality is that institutional interest in financing vehicles for non-Bitcoin assets is minimal. Without structured funding, these companies are left to raise capital through ATM secondary market share issuances—which are inherently dilutive and unsustainable in the absence of capital-efficient tools.
More importantly, the IRR of non-Bitcoin assets is highly uncertain and lacks an institutional-level trust foundation. If ETH or SOL cannot consistently outperform the yield of structured products, capital allocators will not be willing to support this model.
In short: Strategy's model works because Bitcoin has unique financial properties . The possibility of replicating this model on a large scale in other crypto assets is very limited.
Part 4: Core Indicators for Measuring Strategy Execution
Part IV: Key Indicators for Strategic Accountability Tracking
It can be seen that equity issuance is the core of the strategic flywheel. Therefore, tracking the right indicators is crucial to understanding the sustainability and effectiveness of this model. The following four key indicators stand out:
Bitcoin Value Per Share: This is calculated by dividing the total amount of Bitcoin held by the fully diluted number of shares (including convertible bonds, options, and restricted/public stock). Using the fully diluted number of shares ensures consistency and reflects the true potential dilution. This metric shows the amount of Bitcoin effectively supporting the value per share. If a Strategy Strategy company issues shares at a net asset value of 1 or less, the issuance does not increase the value of Bitcoin per share.
mNAV (net asset value multiple): refers to the ratio of a stock's market value to its net asset value. A higher mNAV enables a company to issue shares at a premium, thereby increasing its Bitcoin holdings per share. For reference, MSTR's current mNAV is about 2.24.
mNAV = Market price per share / (Total assets – Total liabilities) ÷ Total shares outstanding
Bitcoin Yield: This metric measures the change in Bitcoin per share over time. This metric is usually updated quarterly or annually to align with earnings reports, but may also be updated immediately after a significant Bitcoin purchase. The Bitcoin Yield reflects how efficiently a company converts raised funds into Bitcoin support per share.
Leverage (%): This is the ratio of a company's total debt to the fair market value of its Bitcoin holdings. It indicates the financial risk that exists on the balance sheet. The target leverage for this strategy should be between 20-30%, and is typically kept around 25%. This allows for some volatility in Bitcoin prices while maintaining financial discipline.
Part 5: BTC Credit Rating Framework
To provide more clarity on the balance sheet, Strategy created a BTC credit rating framework that measures how well Bitcoin backs each liability by comparing BTC net asset value to the notional value of the liability:
BTC rating = BTC net asset value ÷ nominal amount of liabilities
The higher the rating, the more collateral and the lower the risk. If the rating is below 1x, it means that the liabilities are undercollateralized. To quantify this risk, the strategy calculates the BTC risk (i.e. the probability that the BTC rating will be below 1x during the life of the instrument) based on the expected BTC volatility and return.
This risk is then converted into an annualized BTC credit spread:
BTC Credit Spread = – ln (1 – BTC Risk) ÷ Duration
If the spread is below 100 basis points, Strategy considers the instrument investment grade even if the market is pricing it differently. For example, STRF has a BTC rating of 5.8x, BTC risk is only 1%, and BTC ARR is 30%, which means the BTC credit spread is below 100 basis points. This framework helps Strategy benchmark BTC-backed liabilities against traditional credit, providing a basis for eventual credit agency approval and revaluation of MSTR preferred shares.
Part 6: Business Model - Value Creation Machine in the Era of Bitcoin's Rapid Institutionalization
As mentioned above, Strategy is, at its core, a Bitcoin security company. Its business model is novel and its structure is unique, making it unique in the public market. It has three key advantages:
Low-cost, scalable access to capital: The strategy can efficiently raise capital through instruments such as convertible bonds and preferred stocks. While these instruments require future obligations (such as interest or equity dilution), the company incurs minimal immediate cash costs and interest costs. This capital efficiency allows the company to quickly accumulate Bitcoin without being constrained by traditional operating cash flow or profit generation.
Pro-competitive and positive-sum game: This model benefits from wider adoption. As more companies adopt similar strategies, the overall demand for Bitcoin will increase, pushing up its price. In this ecosystem, competition is not a threat, but creates a super positive-sum game.
High tolerance for error: Since Strategy relies on long-term, non-redeemable liquidity, its operation has a high tolerance for error. Even if the timing or execution of the stock issuance is not optimal, the company will not be forced to act under pressure. As long as Bitcoin appreciates over time, just be patient and do nothing, and you can still succeed.
Part VII: Modern Portfolio Management Reform
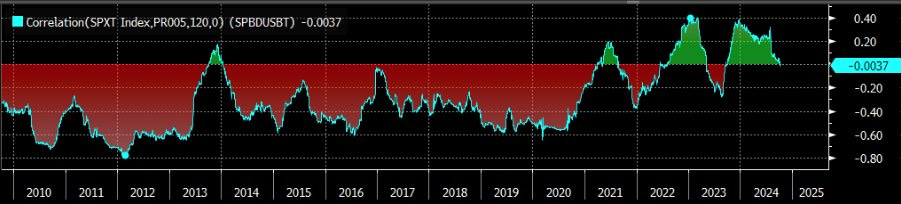
As Jeff Park puts it, “The traditional 60/40 portfolio — 60% in growth stocks and 40% in safe bonds — is no longer relevant.” Bonds have traditionally been viewed as a hedge against equity risk, especially during economic downturns or periods of safe haven. In addition, bonds have long been viewed as a partial hedge against inflation. While cash held by banks loses purchasing power over time, Treasurys at least provide a mechanism to preserve value — albeit an imperfect one.
However, since 2020, the bond market has increasingly deviated from its historical role as a hedge against equity risk. This was particularly evident in 2022, when the S&P 500 (SPY) fell 18% and US Treasuries fell 13%, failing to provide the expected protection. This trend continued into 2024. Moreover, during the recent tariff storm - SPY and QQQ suffered a sharp sell-off - US Treasuries and the US dollar were not snapped up as safe haven assets. Instead, yields soared to nearly 5%, further indicating that US Treasuries are no longer a reliable safe haven.