By ReginaHalf
Source: White55, Mars Finance
Who controls the crypto market ? Six power shifts behind bull and bear markets
On January 3, 2009, Bitcoin 's Genesis Block was successfully mined, marking the first application of blockchain technology to a decentralized digital currency and the official launch of the Bitcoin network. Over the following decade, Bitcoin and the cryptocurrency market it leads have demonstrated a significant long-term bullish trend. However, this journey has been anything but smooth. Its price performance has exhibited dramatic and distinctive cyclical fluctuations, with numerous transitions from frenetic bull markets to deep bear markets . These fluctuations are not random but closely linked to a series of core events that have profoundly impacted the market landscape.
Bitcoin's price trends from 2009 to 2025 (data source: The Block) clearly show six major development stages based on price ranges and fluctuations. The landmark events of each stage and their profound impact on the industry ecosystem are as follows:
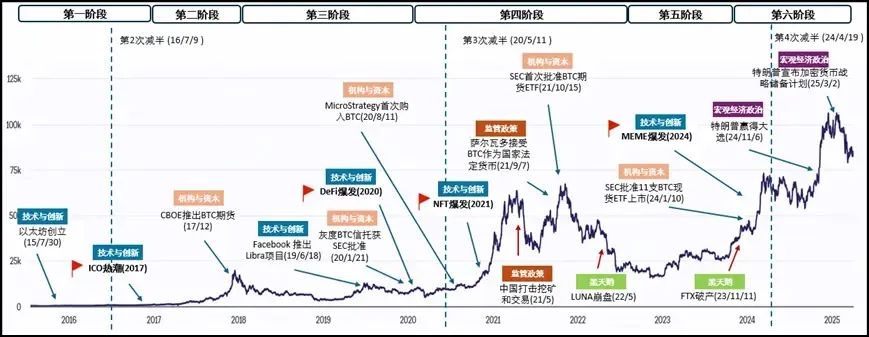
Bitcoin's price trends from 2009 to 2024 demonstrate significant cyclicality. Based on its price range and price fluctuations, it can be divided into six major development stages. The landmark events of each stage and their profound impact on shaping the industry ecosystem are described below:
1. Phase 1 (2009-16): Initial market exploration and technical foundation
In its early days, Bitcoin was little more than a niche toy within the geek community and a testing ground for cryptography enthusiasts. From 2009 to early 2013, its price remained low. However, in 2013, Bitcoin's price experienced its first significant volatility, soaring from around $20 at the beginning of the year to over $1,100 by the end of the year, before falling sharply. This roller-coaster market catapulted Bitcoin into the global spotlight.
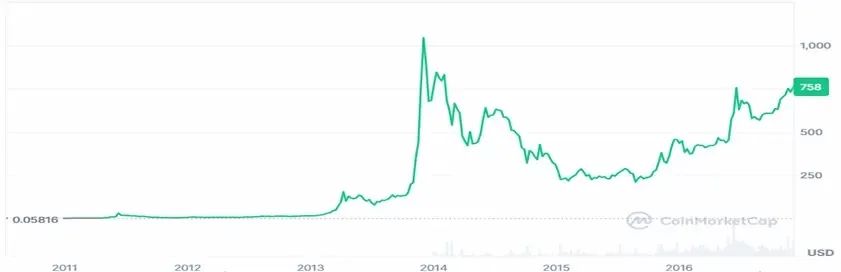
Source: Coingecko
Why did the price of Bitcoin suddenly surge in 2013? The driving factors behind it are as follows:
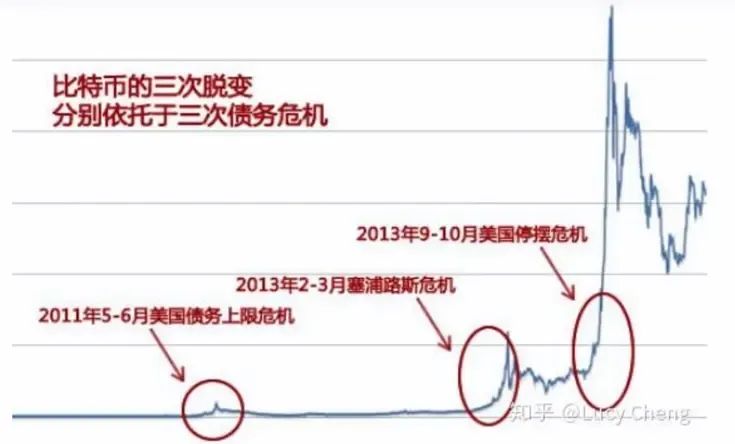
1. Cyprus banking crisis ignites safe-haven demand
In March 2013, the Cypriot government, in exchange for international aid, announced a tax on bank deposits. This radical measure triggered strong public protests, bank runs, and severe market turmoil, profoundly exposing the fragility of the traditional financial system and the potential risks of government policymaking.
Against this backdrop, Bitcoin's decentralized nature and lack of control by a single government led to its first widespread recognition as a potential safe-haven asset. Although Bitcoin's circulation and adoption were still in their early stages, the Cyprus crisis clearly demonstrated the shortcomings of traditional systems. This event served as a catalyst, garnering unprecedented market attention and initial recognition for Bitcoin's value proposition as an alternative asset, particularly its potential as a safe-haven asset.
The Cyprus crisis was not an isolated incident; it occurred against the backdrop of the ongoing global sovereign debt crisis. At the time, several countries were mired in debt, sparking widespread market concerns about the stability of fiat currencies and shaking confidence in them. This ongoing uncertainty created a fertile ground for the growth of non-traditional assets like Bitcoin.
In fact, looking back at 2013, several significant jumps in Bitcoin prices were often closely linked to key risk events in the debt crisis or intensified market panic. This suggests that widespread anxiety about the risks of the traditional financial system was a deep and persistent factor driving the surge in Bitcoin demand and prices that year.
2. Preliminary approval of regulatory policies
Amidst the rapid surge in Bitcoin prices, regulatory policy trends are a key indicator of the industry's future development. On November 18, 2013, the US government held a hearing on the risks and threats posed by Bitcoin and other virtual currencies, publicly recognizing the legality of Bitcoin for the first time.
The clarity of regulatory stance instantly ignited market enthusiasm. The day after the hearing (November 19th), the price of Bitcoin on Mt. Gox, then the world's largest Bitcoin exchange, soared over 114% in a single day, from approximately $420 before the hearing, to break through the $900 mark and shortly thereafter reach a then-all-time high. This surge, triggered by regulatory policy, clearly demonstrated the significant impact of regulatory approval on market confidence and capital inflows.
3. Widespread coverage by mainstream media
In 2013, Bitcoin completely broke out of the tech geek world and became a global mainstream media focus. Major media outlets rushed to report on Bitcoin's soaring price, the tales of early investors getting rich quick, and its disruptive potential. This massively stimulated public interest and speculative enthusiasm, and countless new investors, driven by fear of disappearance, flooded the market, creating a formidable buying force.
However, in 2013, when regulations were favorable and market sentiment was high, why did the price of Bitcoin not continue to soar, but instead entered a downward cycle in 2014?
1. Regulatory risks emerge
In the absence of a strict regulatory framework, the Dark Web, such as Silk Road, flourished thanks to Bitcoin. As a hotbed for untraceable illegal transactions, the Dark Web's rampant money laundering, drug, and contraband trade forced regulators to confront the potential dangers of cryptocurrencies. A landmark event was the FBI's seizure of the first Silk Road in October 2013. This operation not only dealt a heavy blow to the Dark Web ecosystem but also sent a clear signal to the market: Bitcoin is not beyond the law.
2. China tightens regulations
On December 5 of the same year, the People’s Bank of China issued a notice on preventing Bitcoin risks, prohibiting financial institutions from providing Bitcoin-related services. This suppressed Bitcoin’s financial applications in China and caused a sharp drop in Bitcoin prices in the short term.
3. Exchange trust crisis
On February 28, 2014, the Mt. Gox exchange declared bankruptcy and lost a large number of bitcoins, sparking widespread global concerns about exchange security and regulation. Bitcoin prices fell further.
Phase Characteristics: Bitcoin's decentralized nature was prominently demonstrated in Phase 1. Just as the "peer-to-peer electronic cash system" defined in the Bitcoin white paper, its censorship resistance and independent sovereignty were verified in the real world. At the same time, the early immature ecosystem also exposed its vulnerability due to a lack of regulation.
Phase 2 (2016-18): ICO Frenzy and Heavy Regulation
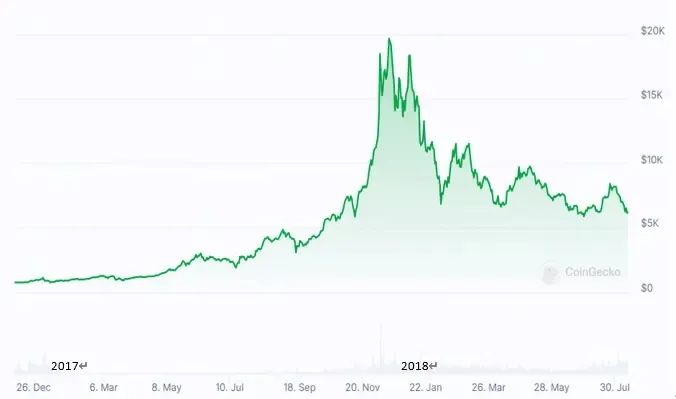
Source: Coingecko
Breakthrough in the crypto ecosystem
On July 20, 2015, the Ethereum mainnet was launched. The smart contracts and decentralized application framework it introduced expanded blockchain technology from a single payment scenario to the entire ecosystem including finance, gaming, and social networking, marking the official start of the technological revolution of the value Internet.
Along with technological innovation, Bitcoin's internal mechanisms began to take effect: the second block reward halving occurred on July 9, 2016. The expected scarcity, coupled with the incremental capital brought by the Ethereum ecosystem, jointly pushed the market out of its trough at the end of 2016 and ushered in a new round of recovery.
With the maturity of Ethereum's smart contract technology, the global ICO market experienced explosive growth in 2017. By the end of November of that year, a total of 430 ICO projects had been launched worldwide, raising a total of US$4.6 billion. Taking the Chinese market as an example, a 2017 research brief from the Tsinghua University National Institute of Finance shows that domestic ICO financing reached 2.6 billion RMB in the first half of the year alone, with over 100,000 investors participating, reflecting a significant increase in market participation.
This trend is driven by two factors:
For project owners, ICOs provide a financing channel that circumvents the strict scrutiny of traditional IPOs. Funds can be raised with only basic technical documentation, while avoiding the issue of equity dilution.
For ordinary investors, participating in early-stage projects with low barriers to entry and obtaining short-term premium returns after the tokens are listed constitutes a strong speculative motivation.
However, market expansion is accompanied by the accumulation of systemic risks. ICO projects generally lack information disclosure mechanisms and qualification review standards, and there are no clear regulations on fundraising scales and circulation methods. In the absence of regulation, financing has expanded unchecked from core blockchain technology development to areas such as the Internet of Things, gambling, and social media. More seriously, the technical security risks of smart contracts continue to be exposed, further amplifying market risks.
Heavy regulatory blow and market turning point
In response to these issues, on September 4, 2017, the People's Bank of China, along with seven other ministries and commissions, issued the "Announcement on Preventing Risks in Token Issuance and Financing," explicitly defining ICOs as illegal public financing activities. This ban required domestic cryptocurrency exchanges to halt trading and shut down their platforms by September 15, leading to a sharp drop in virtual currency market trading volume and a simultaneous sharp decline in Bitcoin prices. This regulatory action marked a paradigm shift in global governance regarding decentralized finance.
Phase Characteristics: In the second phase, we can see that Ethereum's technological innovation drove explosive market growth. However, the absence of macroeconomic regulation led to the accumulation of risks. This process reveals the two-way interaction of macroeconomic dynamics: technology and innovation provide the momentum for market growth, while the restructuring of the regulatory system guides the direction of market correction.
III. The third phase (2018-20): Market clearing and institutional breakthroughs
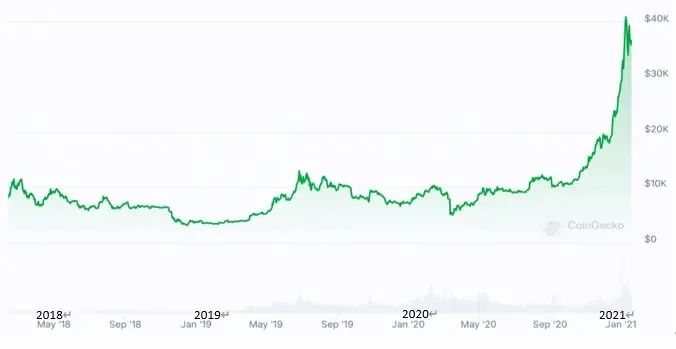
Source: Coingecko
Deep pullback and market clearing
After the 2017 ICO bubble burst, the Bitcoin market entered a deep correction in 2018, with numerous projects going bankrupt and liquidating, putting continued pressure on prices. By early 2020, Bitcoin prices had remained range-bound around $10,000. The key turning point during this period was the entry of traditional capital and regulatory compliance institutions, laying the foundation for a new bull market and ultimately igniting a wave of innovation in decentralized finance ( DeFi ) in the summer of 2020.
Institutional entry
On June 18, 2019, Facebook officially released the Libra stablecoin white paper, attempting to build a global digital currency payment network. This disruptive challenge to the traditional financial system was ultimately shelved due to political opposition from global regulators.
On January 21, 2020, Grayscale Bitcoin Trust completed registration with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), becoming the first SEC-regulated cryptocurrency investment vehicle. General Manager Michael Sonnenshein emphasized, "Grayscale voluntarily accepted this designation and will continue to work within the existing regulatory framework. Today's announcement should signal to investors that our regulators are willing to engage with our products and the entire (cryptocurrency) industry." This move provides a compliant onboarding channel for institutional capital, significantly lowering the investment threshold.
On August 11, 2020, MicroStrategy purchased its first 21,454 Bitcoins for $250 million. Today (2025), MicroStrategy is one of the world's largest public Bitcoin holders. MicroStrategy's Bitcoin acquisition strategy has fundamentally changed the way businesses think about financial management and transformed the industry's approach to digital assets.
Phase Characteristics: The third phase is a critical period of market self-recovery and transformation. In the bear market following the ICO bubble burst, inferior projects were eliminated. The entry of real-world institutions provided a path for institutionalization in the crypto market, paving the way for the next phase of market explosion.
4. The fourth stage (2020-22): Defi expansion, NFT outbreak and regulatory differentiation
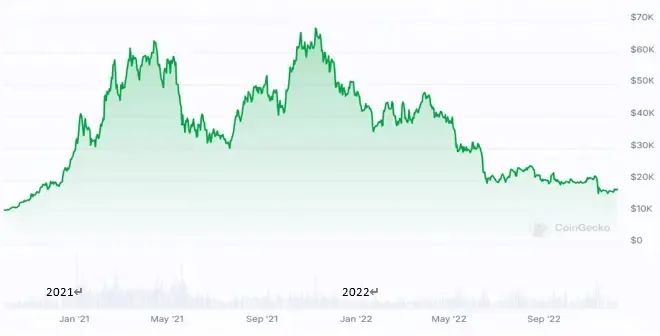
Source: Coingecko
The DeFi ecosystem is growing exponentially
Based on the composability innovations of Ethereum smart contracts, decentralized finance (DeFi) entered a period of explosive growth in the summer of 2020. Core indicators showed exponential growth. According to DeFi Llama, the industry's total value locked (TVL) soared from approximately $15 billion at the beginning of 2021 to a peak of nearly $180 billion by the end of the year, a year-over-year increase of 1,100%. Thousands of protocols emerged during this process, reshaping traditional financial logic. Representative projects with infrastructural significance include:
Compound, a collateralized lending protocol
Automated Market Maker Uniswap
Stable currency system USDT
Decentralized Oracle ChainLink
Synthetix, a synthetic asset platform
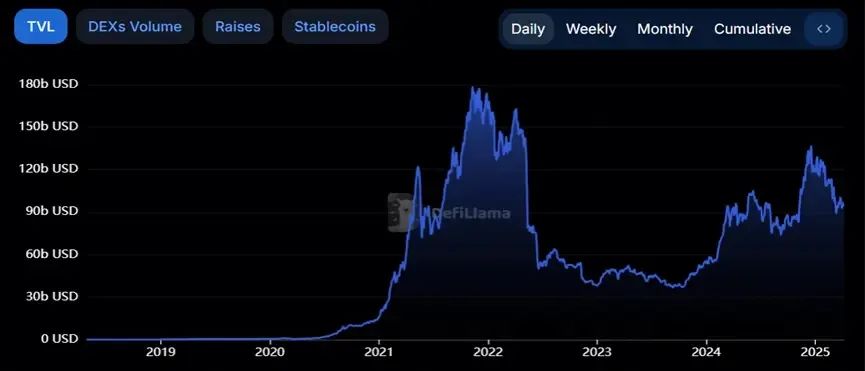
NFT market explodes
During the same period, the non-fungible token (NFT) market transitioned from technological experimentation to mainstream consumption. Its core breakthrough lies in enabling unique on-chain ownership of digital content through the ERC-721/1155 standard, spawning trillion-dollar emerging markets such as art, collectibles, and virtual real estate. Case studies such as CryptoPunks, BAYC, and Decentraland signal a fundamental shift in the ownership economic paradigm.
Global regulatory stances diverge significantly
In the fourth stage, the regulatory stances of various countries towards cryptocurrencies are diverging:
China
May 2021: The Financial Stability and Development Committee of the State Council explicitly called for a "crackdown on Bitcoin mining and trading activities," and mining hubs such as Inner Mongolia and Xinjiang began to clear out businesses.
September 2021: The People's Bank of China and ten other ministries and commissions issued the "Notice on Further Preventing and Dealing with the Risks of Virtual Currency Transaction Speculation", classifying virtual currency-related businesses as "illegal financial activities" and comprehensively prohibiting the provision of services within the country.
El Salvador
On June 8, 2021, the El Salvador Legislative Assembly voted to establish Bitcoin as an unrestricted legal tender, making the Republic of El Salvador the first country to officially adopt cryptocurrency.
USA
On October 15, 2021, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) approved the listing of the ProShares Bitcoin Futures ETF (ticker: BITO) on the New York Stock Exchange. This move marks the first time that the traditional financial system has embraced cryptocurrency derivatives, creating a standardized channel for institutional capital allocation.
Characteristics of this stage: Technological innovation has driven the market to unprecedented prosperity, but the pressure for regulatory adaptation has increased significantly after the peak of the bull market, and the regulatory paths of various countries have shown significant differences.
5. The fifth phase (2022-24): Black swan impact and governance reconstruction
Source: Coingecko
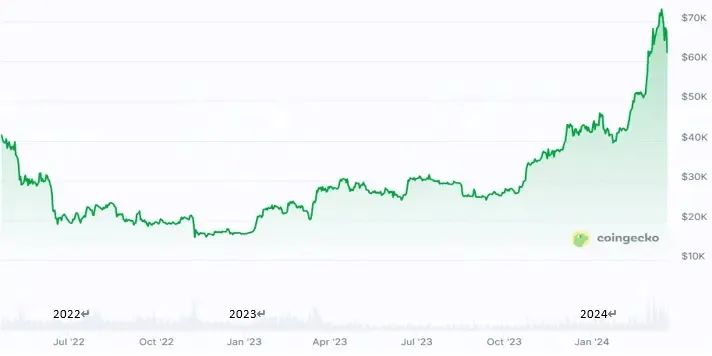
Chain risk events and deep downturn
Driven by a series of risk events, including the LUNA crash, Celsius bankruptcy, and FTX closure, the cryptocurrency market fell into a deep downturn in 2023. Bitcoin prices continued to decline since the end of 2022, falling below $20,000 by early 2023.
In May 2022, the Terra ecosystem collapsed, causing a significant decoupling of its algorithmic stablecoin, UST, and consequently destroying the value of the LUNA token. This incident triggered a systematic rethinking of the decentralized stablecoin economic model. Panic spread throughout the stablecoin market, and mainstream stablecoins such as USDT were temporarily subject to a run.
Celsius, a crypto lending institution, was one of the first crypto institutions to be affected by the collapse of TerraUSD and Luna, filing for bankruptcy in July 2022. This forced regulators to accelerate the formulation of regulatory requirements for lending platforms.
The FTX exchange's bankruptcy in November 2022 triggered a crisis of trust within exchanges, becoming a black swan event that crushed market confidence. This event heightened market expectations for transparency and trust in exchanges, prompting industry reflection and improvement.
Characteristics of this phase: A series of black swan events exposed the industry's problems in risk management, transparency, and governance, forcing the market into a bear market. This forced the market to undergo a painful but necessary liquidation, and promoted the industry's reflection and upgrading of safety, transparency, and regulatory compliance.
VI. Phase 6 (2024-25): Institutional Breakthrough and Macro-Narrative Resonance
Source: Coingecko
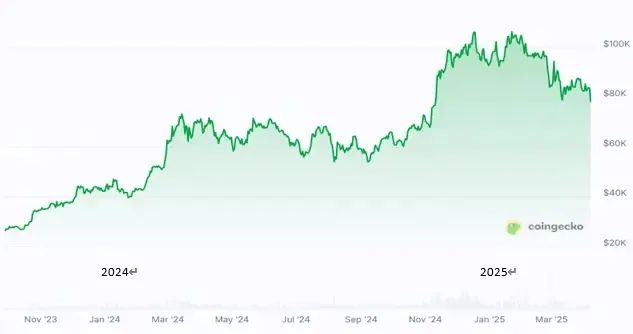
Market recovery and historic breakthrough
Driven by regulatory compliance and a shift in monetary policy, the cryptocurrency market achieved a historic breakthrough in 2024. Bitcoin's price broke through $100,000 for the first time, Ethereum significantly improved its Layer 2 scalability through the Cancun upgrade, and the meme coin sector simultaneously experienced explosive growth.
In January 2024, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) approved the listing of 11 BTC spot ETFs. This massive influx of funds from traditional institutions into the crypto market further promoted its compliance development. In May of the same year, an Ethereum spot ETF was approved.
In September 2024, the Federal Reserve cut interest rates by 50 basis points for the first time in four years. This move promoted the transfer of funds in traditional markets to high-risk assets, and a large amount of liquidity was injected into the crypto market.
In November 2024, Trump was elected President of the United States. His public support for cryptocurrency pushed the price of Bitcoin to over $100,000.
Characteristics of this stage: Institutional breakthroughs resonate with macroeconomic policies and political narratives, pushing the market into a new round of growth cycle dominated by institutions and more compliant.
VII. Summary
The growth cycles of Bitcoin's price offer a glimpse into the dynamics of the cryptocurrency market. The cryptocurrency market follows a cyclical pattern: "technological innovation bursts à market speculation frenzy à regulatory intervention à deep market correction à iteration of underlying technology." The factors influencing the market are diverse and mutually reinforcing, with the core factors including the following:
Technological innovation and ecosystem development: The continued expansion of application scenarios such as Ethereum smart contracts, DeFi protocols, NFTs, and GameFi is one of the core drivers of attracting capital and users. Meanwhile, Bitcoin's four-year halving, by reducing supply, has long-term supported upward price expectations.
Driven by market sentiment and speculation: The emergence of a new round of narratives, the development of technology and ecology, accompanied by rising coin prices, have amplified users' FOMO emotions, triggered a speculative frenzy, and driven up prices.
Regulatory policies and compliance progress: China halted ICOs, El Salvador designated Bitcoin as legal tender, and the US approved Bitcoin futures and spot ETFs. These policy changes have directly impacted market confidence and capital flows. While stricter regulation may suppress the market in the short term, compliance will ultimately clear the way for large-scale institutional capital to enter the market, promoting market standardization and mainstream adoption.
Institutional and capital entry: Grayscale Trust, MicroStrategy, spot ETFs and other channels have lowered the entry threshold for traditional capital, and their large-scale influx has provided stability endorsement and continuous liquidity to the market.
Macroeconomic and political environment: Global monetary policies, geopolitical risks, major political events, and leaders' policy preferences significantly amplify market volatility, and cryptocurrencies are increasingly demonstrating their potential as macro hedging tools.
Black swan events and market corrections: The collapse of Mt. Gox, the collapse of LUNA, and the bankruptcy of FTX triggered a crisis of trust and a bear market correction. However, these crises also prompted market reflection, eliminated inferior projects, and promoted improved security, transparency, and governance standards, laying the foundation for the next round of healthy development.
At the same time, we can find that:
The cryptocurrency market follows a spiral cycle, and each cycle eliminates inferior projects and ecosystems while accumulating high-quality value.
Breakthroughs in blockchain technology and ecological expansion are the core engines of long-term value growth in the cryptocurrency market.
Regulatory policies are a double-edged sword for market development, and the final compliance process (such as spot ETFs) is the only way to attract institutional capital and achieve mainstreamization, marking a leap in market maturity.
The impact of global macroeconomics, monetary policy and geopolitics on crypto market volatility is becoming increasingly significant, and its macro attributes as a new asset class are enhanced.
Although black swan events cause short-term pain, they objectively accelerate the standardized development of the industry in terms of security, transparency and governance.
At the beginning of a new cycle in 2025, the tokenization of real-world assets (RWA) is emerging as a bridge connecting traditional finance and the on-chain ecosystem, signaling a potential shift in market focus from speculative frenzy to more substantial value creation. In the foreseeable future, the cryptocurrency market will enter a new era of dual-growth driven by institutional innovation and continuous technological breakthroughs.